Configuring a DHCP Server
Networking Fundamentals, Configuration and Management, Documentation and Planning, Troubleshooting
Contents
Scenario
In this Packet Tracer Lab, I will setup a DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server to dynamically allocate IP addressing information to hosts within a simple network.
DHCP is a network management protocol used to automate the process of configuring devices on IP networks. It allows devices to obtain necessary network parameters, such as IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS servers, automatically from a DHCP server. This eliminates the need for manual configuration of IP settings on each device.
The main benefit of using DHCP is that it ensures efficient use of IP addresses by dynamically allocating them to devices as needed. This helps avoid conflicts and makes better use of the available address space.
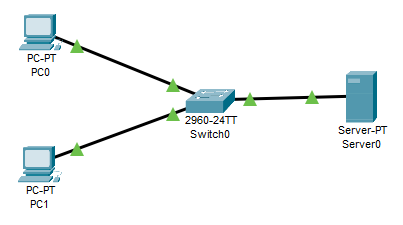
This is the network topology I will be using:
Objectives
- Add a new address pool to the DHCP server
- Configure the hosts to obtain information via DHCP
- Confirm hosts received IP information via DHCP
Results
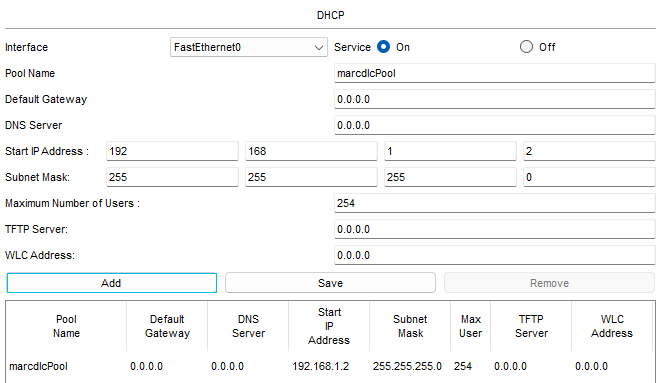
📄 Task 1: Add a new address pool to the DHCP server
I configure a new IP address pool in the DHCP server starting with address 192.168.1.2 and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0. This means there are a total of 254 assignable host addresses.
📄 Task 2: Configure the hosts to obtain information via DHCP
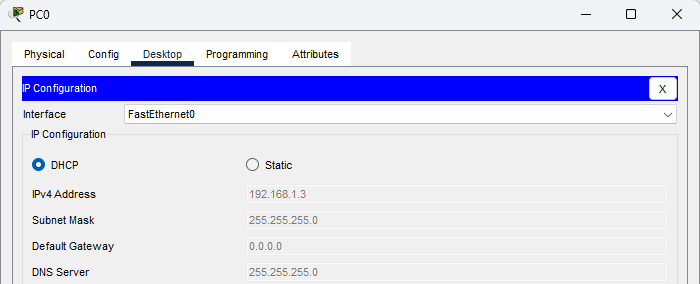
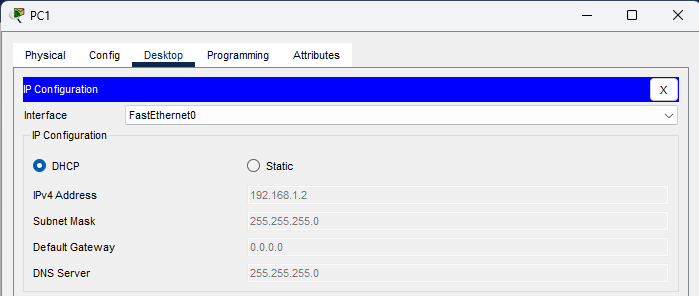
For each host in the network, I configure them to receive IP information from the DHCP server. After a few seconds, the hosts receive an IP address and a subnet mask.
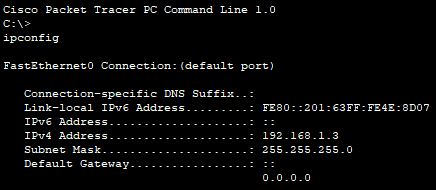
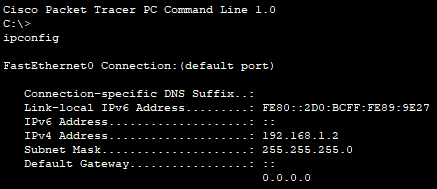
📄 Task 3: Confirm hosts received IP information via DHCP
I use the ipconfig command to confirm that each host has received IP information from the DHCP server.
 —
—